Networking Protocols
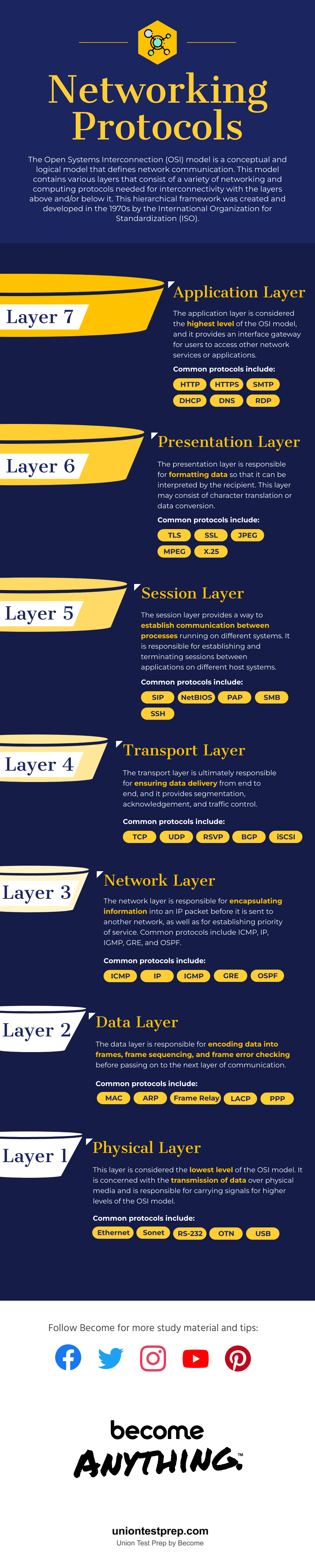
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual and logical model that defines network communication. This model contains various layers that consist of a variety of networking and computing protocols needed for interconnectivity with the layers above and/or below it. This hierarchical framework was created and developed in the 1970s by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Layer 7 - Application layer
The application layer is considered the highest level of the OSI model, and it provides an interface gateway for users to access other network services or applications. Common protocols include HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, DHCP, DNS, and RDP.
Layer 6 - Presentation Layer
The presentation layer is responsible for formatting data so that it can be interpreted by the recipient. This layer may consist of character translation or data conversion. Common protocols include TLS, SSL, JPEG, MPEG, and X.25.
Layer 5 - Session layer
The session layer provides a way to establish communication between processes running on different systems. It is responsible for establishing and terminating sessions between applications on different host systems. Common protocols include SIP, NetBIOS, PAP, SMB, and SSH.
Layer 4 - Transport Layer
The transport layer is ultimately responsible for ensuring data delivery from end to end, and it provides segmentation, acknowledgement, and traffic control. Common protocols include TCP, UDP, RSVP, BGP, and iSCSI.
Layer 3 - Network Layer
The network layer is responsible for encapsulating information into an IP packet before it is sent to another network, as well as for establishing priority of service. Common protocols include ICMP, IP, IGMP, GRE, and OSPF.
Layer 2 - Data Layer
The data layer is responsible for encoding data into frames, frame sequencing, and frame error checking before passing on to the next layer of communication. Common protocols include MAC, ARP, Frame Relay, LACP, and PPP.
Layer 1 - Physical Layer
This layer is considered the lowest level of the OSI model. It is concerned with the transmission of data over physical media and is responsible for carrying signals for higher levels of the OSI model. Common protocols include Ethernet, SONET, RS-232, OTN, and USB.
Keep Reading
Computing Technology Industry Association A+ Core Series Exam Blog
What’s in the 2022 CompTIA A+ Core Series Exam Revision?
Every three years, the CompTIA exam is revised. This is not surprising …

Computing Technology Industry Association A+ Core Series Exam Blog
Is the CompTIA A+ Worth It?
While other industries are scrambling to stay afloat in today’s tumultu…

Computing Technology Industry Association A+ Core Series Exam Blog
How to Design an Effective Password Policy
A password policy is a set of rules that are placed on password creatio…