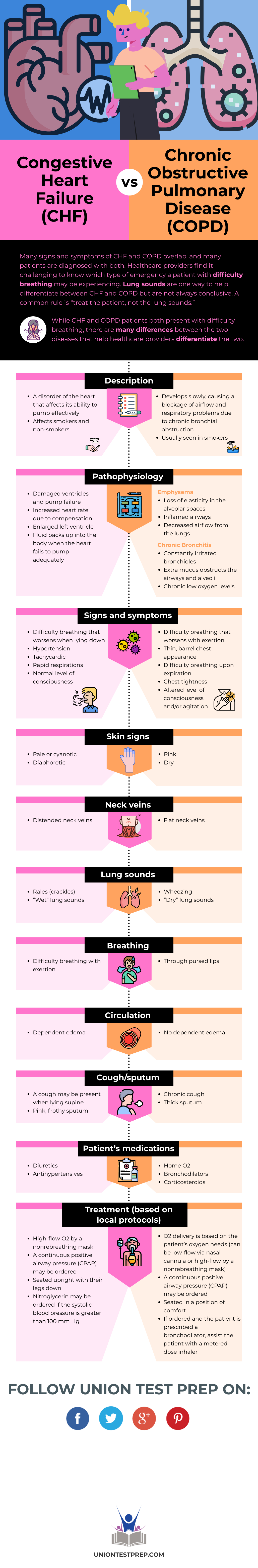
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) vs. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Many signs and symptoms of CHF and COPD overlap, and many patients are diagnosed with both. Healthcare providers find it challenging to know which type of emergency a patient with difficulty breathing may be experiencing. Lung sounds are one way to help differentiate between CHF and COPD but are not always conclusive. A common rule is “treat the patient, not the lung sounds.”
While CHF and COPD patients both present with difficulty breathing, there are many differences between the two diseases that help healthcare providers differentiate the two.
| CHF | COPD | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | - A disorder of the heart that affects its ability to pump effectively - Affects smokers and non-smokers |
- Develops slowly, causing a blockage of airflow and respiratory problems due to chronic bronchial obstruction - Usually seen in smokers |
| Pathophysiology | - Damaged ventricles and pump failure - Increased heart rate due to compensation - Enlarged left ventricle - Fluid backs up into the body when the heart fails to pump adequately |
Emphysema - Loss of elasticity in the alveolar spaces - Inflamed airways - Decreased airflow from the lungs Chronic Bronchitis - Constantly irritated bronchioles - Extra mucus obstructs the airways and alveoli - Chronic low oxygen levels |
| Signs and symptoms | - Difficulty breathing that worsens when lying down - Hypertension - Tachycardia - Rapid respirations - Normal level of consciousness |
- Difficulty breathing that worsens with exertion - Thin barrel chest appearance - Difficulty breathing upon expiration - Chest tightness - Altered level of consciousness and/or agitation |
| Skin signs | - Pale or cyanotic - Diaphoretic |
- Pink - Dry |
| Neck Veins | - Distended neck veins | - Flat neck veins |
| Lung sounds | - Rales (crackles) - “Wet” lung sounds |
- Wheezing - “Dry” lung sounds |
| Breathing | - Difficulty breathing with exertion |
- Through pursed lips |
| Circulation | - Dependent edema | - No dependent edema |
| Cough/sputum | - A cough may be present when lying supine - Pink frothy sputum |
- Chronic cough - Thick sputum |
| Patient’s medications | - Diuretics - Antihypertensives |
- Home \(\text{O}_2\) - Bronchodilators - Corticosteroids |
| Treatment (based on local protocols) |
- High-flow \(\text{O}_2\) by a non-rebreathing mask - A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) may be ordered - Seated upright with their legs down - Nitroglycerin may be ordered if the systolic blood pressure is greater than 100 mm Hg |
- \(\text{O}_2\) delivery is based on the patient’s oxygen needs (can be low-flow via nasal cannula or high-flow by a non- rebreathing mask - A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) may be ordered - Seated in a position of comfort If ordered and the patient is prescribed a bronchodilator, assist the patient with a metered-dose inhaler |
Keep Reading

Emergency Medical Technician Test Blog
How Many Questions are on the NREMT?
The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) exam is …

Emergency Medical Technician Test Blog
How Hard is the EMT Test?
EMTs (Emergency Medical Technicians) are required to have strong medica…

Emergency Medical Technician Test Blog
What Is a Passing Score on the NREMT Exam?
The job outlook for EMTs and paramedics is strong. The Bureau of Labor …