Commonly Used Organ-Specific Medications
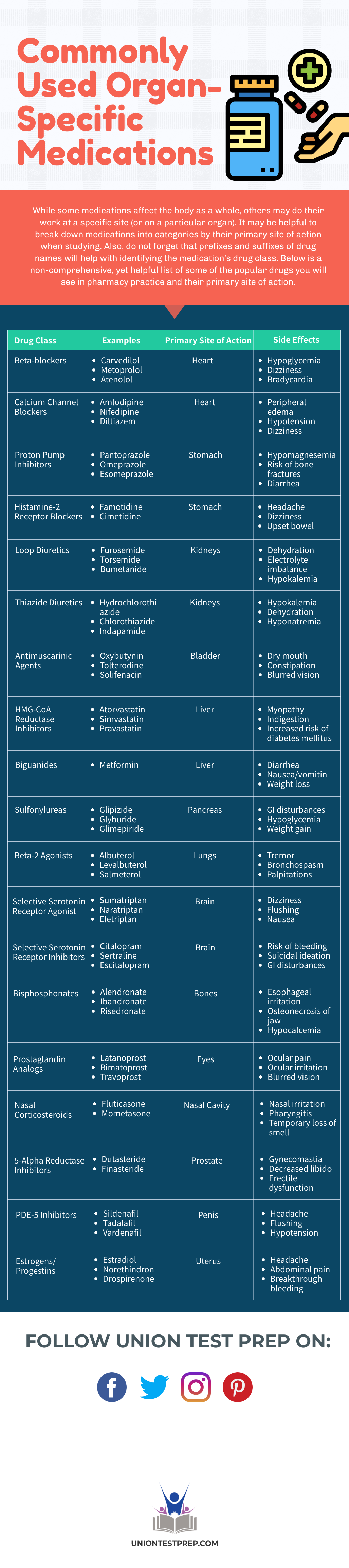
While some medications affect the body as a whole, others may do their work at a specific site (or on a particular organ). It may be helpful to break down medications into categories by their primary site of action when studying. Also, do not forget that prefixes and suffixes of drug names will help with identifying the medication’s drug class. Below is a non-comprehensive, yet helpful list of some of the popular drugs you will see in pharmacy practice and their primary site of action.
| Drug Class | Examples | Primary Site of Action | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-blockers | Carvedilol Metoprolol Atenolol |
Heart | Hypoglycemia Dizziness Bradycardia |
| Calcium Channel Blockers |
Amlodipine Nifedipine Diltiazem |
Heart | Peripheral edema Hypotension Dizziness |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors |
Pantoprazole Omeprazole Esomeprazole |
Stomach | Hypomagnesemia Risk of bone fractures Diarrhea |
| Histamine-2 Receptor Blockers |
Famotidine Cimetidine |
Stomach | Headache Dizziness Upset bowel |
| Loop Diuretics | Furosemide Torsemide Bumetanide |
Kidneys | Dehydration Electrolyte imbalance Hypokalemia |
| Thiazide Diuretics | Hydrochlorothiazide Chlorothiazide Indapamide |
Kidneys | Hypokalemia Dehydration Hyponatremia |
| Antimuscarinic Agents |
Oxybutynin Tolterodine Solifenacin |
Bladder | Dry mouth Constipation Blurred vision |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors |
Atorvastatin Simvastatin Pravastatin |
Liver | Myopathy Indigestion Increased risk of diabetes mellitus |
| Biguanides | Metformin | Liver | Diarrhea Nausea/vomiting Weight loss |
| Sulfonylureas | Glipizide Glyburide Glimepiride |
Pancreas | GI disturbances Hypoglycemia Weight gain |
| Beta-2 Agonists | Albuterol Levalbuterol Salmeterol |
Lungs | Tremor Bronchospasm Palpitations |
| Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists |
Sumatriptan Naratriptan Eletriptan |
Brain | Dizziness Flushing Nausea |
| Selective Serotonin Receptor Inhibitors |
Citalopram Sertraline Escitalopram |
Brain | Risk of bleeding Suicidal ideation GI disturbances |
| Bisphosphonates | Alendronate Ibandronate Risendronate |
Bones | Esophageal irritation Osteonecrosis of jaw Hypocalcemia |
| Prostaglandin Analogs |
Latanoprost Bimatoprost Travoprost |
Eyes | Ocular pain Ocular irritation Blurred vision |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Fluticasone Mometasone |
Nasal Cavity | Nasal irritation Pharyngitis Temporary loss of smell |
| 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors |
Dutasteride Finasteride |
Prostate | Gynecomastia Decreased libido Erectile dysfunction |
| PDE-5 Inhibitors | Sildenafil Tadalafil Vardenafil |
Penis | Headache Flushing Hypotension |
| Estrogens/Progestins | Estradiol Norethindrone Drospirenone |
Uterus | Headache Abdominal pain Breakthrough bleeding |
Although memorizing the top 200 medications along with their characteristics may seem daunting, breaking them down by drug class as well as their primary site of action will make studying more manageable. It is also important to take note of the side effect profile of these drugs. If side effects become too severe or bothersome to a patient, it might warrant discontinuation of the medication and a change in therapy.
Keep Reading
PTCB Pharmacy Technician Certification Exam Blog
Memorable Mnemonics: Master Drug Knowledge for the PTCB Exam
Studying for the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) exam is…
PTCB Pharmacy Technician Certification Exam Blog
The Top 200 Drugs on the PTCB
The Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) exam is the final st…

PTCB Pharmacy Technician Certification Exam Blog
Is the PTCB Exam Hard?
Is the PTCB Exam Hard? Did you know that in 2021, over 430,000 pharmac…