Formulas You’ll Need for the ASVAB General Science Test
If you want to enlist in the military, or if you’re taking a vocational test at your school, you’ll need to know which are your best skills, and the ASVAB General Science Test is designed to discover your science-related skills, in areas like problem-solving, strategical thinking, and abstraction. The General Science section covers a lot of different content at a very basic level, and we have designed a formula sheet for you with the most basic formulas you’ll need to solve problems while taking this test.
Although you won’t be able to use this sheet during the actual test, you can use it to prepare, and practice by working on the practice questions for the ASVAB General Science Test at Union Test Prep, or dig deeper by consulting our Study Guide for the ASVAB General Science Test!
Physics
| Formula | Symbols |
|---|---|
| \(w = m \cdot g\) | \(w= \text{weight } (N)\) \(m = \text{mass } (kg)\) \(g = \text{gravity } (m/s^2)\) |
| \(v = \dfrac{d}{t}\) | \(v = \text{speed } (m/s)\) \(d= \text{distance } (m)\) \(t= \text{time } (s)\) |
| \(v = v_o +a \cdot t\) | \(v = \text{speed } (m/s)\) \(v_o = \text{initial speed } (m/s)\) \(a = \text{acceleration } (m/s^2)\) \(t = \text{time } (s)\) |
| \(x = x_o + v_o \cdot t + \frac{1}{2} a \cdot t^2\) | \(x = \text{position } (m)\) \(x_o = \text{initial position } (m)\) \(v_o = \text{initial speed } (m/s)\) \(t = \text{time } (s)\) \(a = \text{acceleration } (m/s^2)\) |
| \(v^2 = (v_o)^2+2a \cdot (x-x_o)\) | \(v= \text{speed } (m/s)\) \(v_o = \text{initial speed } (m/s)\) \(a = \text{acceleration } (m/s^2)\) \(x = \text{position } (m)\) \(x_o = \text{initial position } (m)\) |
| \(f = m\cdot a\) | \(f = \text{force } (N)\) \(m = \text{mass } (kg)\) \(a = \text{acceleration } (m/s^2)\) |
| \(PE_g = m \cdot g \cdot h\) | \(PE_g = \text{Gravitational Potential Energy } (J)\) \(m = \text{mass } (kg)\) \(g = \text{gravity } (m/s^2)\) \(h = \text{height } (m)\) |
| \(KE = \frac{1}{2} \cdot m \cdot v^2\) | \(KE = \text{Kinetic Energy } (J)\) \(m = \text{mass } (kg)\) \(v = \text{velocity } (m/s)\) |
| \(F = k \cdot \dfrac{ q_1 \cdot q_2}{r^2}\) | \(F = \text{Electric Force } (N)\) \(k = \text{Coulomb's Constant} = 8.988 \times 10^9 \; Nm^2/C^2\) \(q_n = \text{Charge }n \; (C)\) \(r = \text{Distance between charges } (m)\) |
| \(n = \dfrac{c}{a}\) | \(n = \text{refractive index }\) \(c = \text{speed of light in the vacuum } (m/s)\) \(a = \text{speed of light in a medium } (m/s)\) |
| \(\lambda = \dfrac{c}{f}\) | \(\lambda = \text{wavelength }(m)\) \(c = \text{speed of light } (m/s)\) \(f = \text{frequency } (1/s)\) |
| \(Q = m\cdot s \cdot \Delta t\) | \(Q = \text{Transferred Heat } (J)\) \(m = \text{mass } (g)\) \(s = \text{specific heat } (J/g \cdot K)\) \(\Delta t = \text{change in temperature } (K)\) |
| \(B = \dfrac{\mu_o I}{2\pi r}\) | \(B = \text{Magnetic field magnitude } (T)\) \(\mu_o = \text{permeability of free space } (T \cdot m/A)\) \(I = \text{Magnitude of the electric current } (A)\) \(\pi \approx 3.14\) \(r = \text{distance } (m)\) |
| \(B_s = \mu_o \cdot I \cdot n\) | \(B_s = \text{Magnetic field in a solenoid } (T)\) \(\mu_o = \text{permeability of free space } (T \cdot m/A)\) \(I = \text{Magnitude of the electric current } (A)\) \(n = \text{number of turns per unit length }\) |
Chemistry
| Formula | Symbols |
|---|---|
| \(A = Z + N\) | \(A = \text{Mass Number}\) \(Z = \text{Atomic Number = Number of Protons}\) \(N = \text{Number of Neurons}\) |
| \(pH = -\log[H_3O^+]\) | \(pH = \text{decimal cologarithm of Hydrogen}\) \([H_3O^+] = \text{Hydronium concentration } (mole/L)\) |
| \(14 = pH + pOH\) | \(pH = \text{decimal cologarithm of Hydrogen}\) \(pOH = \text{decimal cologarithm of Hydroxide}\) |
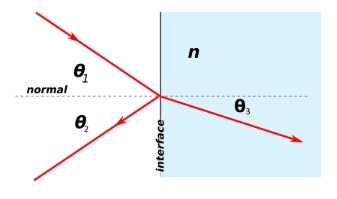
Formulas using the above figure:
Formula 1:
\[\theta_1 = \theta_2\]where
\[\theta_1 = \text{angle of incident ray}\] \[\theta_2 = \text{angle of reflection}\]Formula 2:
\[n_1 \cdot \sin(\theta_1) = n \cdot \sin(\theta_3)\]where
\[n_1 = \text{refractive index of medium 1}\] \[\theta_1 = \text{angle of incident ray}\] \[n = \text{refractive index of medium }n\] \[\theta_3 = \text{angle of refraction}\]Keep Reading

Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery Blog
What is the ASVAB Test?
The Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery, known as the ASVAB, is …

Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery Blog
Military MOS Codes
Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) codes are an integral part of the…

Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery Blog
U.S. Army Height and Weight Standards for Females
The U.S. Army’s commitment to maintaining a robust, physically fit, and…